Blog
How to Choose the Right Knife Gate Valve for Your Application?
When selecting a knife gate valve for your application, key considerations arise. John Smith, a renowned expert in valve engineering, once stated, “The right valve makes all the difference.” This resonates deeply in the realm of knife gate valves, where choices span numerous factors.
Knife gate valves are designed for on/off flow control. They excel in industries like wastewater treatment and mining. Their unique construction allows them to manage slurries effectively. However, not all knife gate valves are the same. You must evaluate material compatibility, pressure ratings, and media types to make an informed decision.
Moreover, installation and maintenance cannot be overlooked. It is crucial to consider where and how the valve will be used. While many options are available, identifying your specific needs can be challenging. Relying solely on standard specifications might lead to costly mistakes down the line. Every application is unique, requiring a tailored approach to choosing the best knife gate valve.
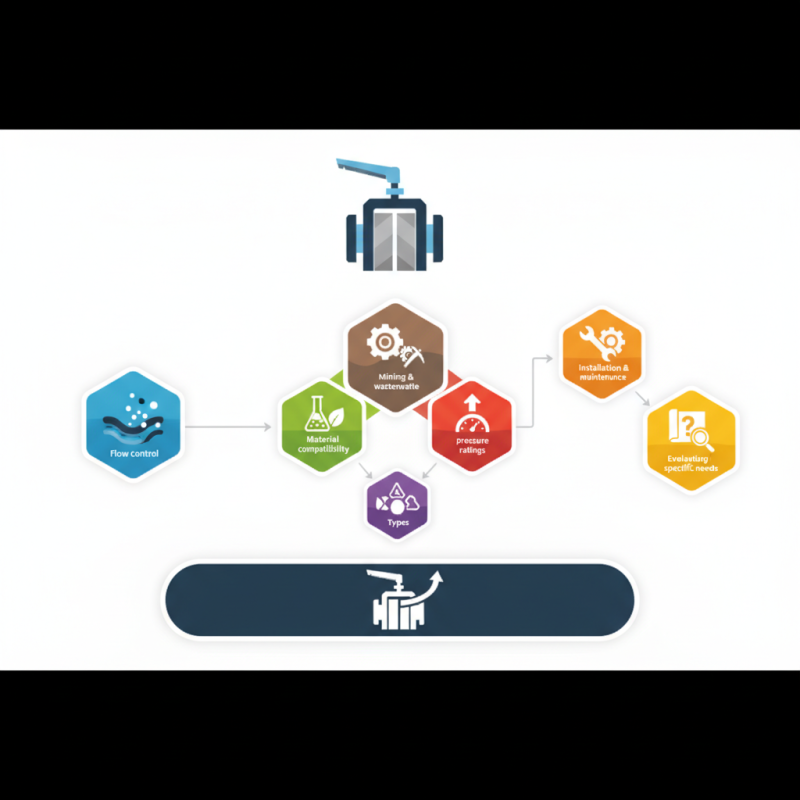
Understanding Knife Gate Valves and Their Applications
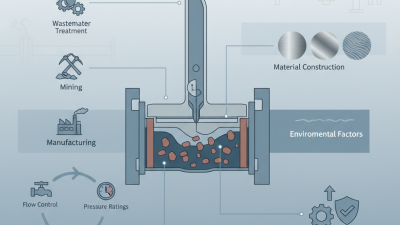
Knife gate valves are essential in various industrial applications. They excel in handling slurries, powders, and bulk solids. These valves operate through a sharp-edged gate that shears through materials, ensuring a tight seal. According to a report by Global Market Insights, the market for knife gate valves is expected to grow by over 5% annually. This growth is driven by their efficiency in industries such as mining and sewage treatment.
Selecting the right knife gate valve requires understanding the specific application. Factors like pressure, temperature, and flow medium are vital. Many industries face challenges with material buildup or corrosion. These issues can compromise valve performance. A study on valve performance noted that improper selection can lead to a 30% increase in maintenance costs.
Installation and maintenance are significant considerations too. Regular inspections can detect issues early. However, many operators overlook this step. A lack of proper training can result in incorrect handling, impacting efficiency. In a survey, 40% of respondents admitted to insufficient training on valve operations. This gap can lead to unexpected downtime and increased operational risks.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Knife Gate Valves

Choosing the right knife gate valve requires careful consideration of several factors. One key aspect is the type of media the valve will handle. If the media is abrasive or contains solids, you need a robust valve that can withstand wear. Check the valve's construction materials to ensure durability.
Another factor is the pressure and temperature conditions of your application. Knife gate valves are available in various pressure ratings, so it's crucial to select one that meets your requirements. A valve designed for high-pressure applications can fail if used in low-pressure settings. Be mindful of the operational environment; extreme temperatures can impact valve performance.
Tips: Always consult with industry experts when in doubt. Perform a thorough research on both material specifications and operational capabilities. Don't overlook the importance of maintenance; a poorly maintained valve can lead to frequent breakdowns and increased costs.
Consider the installation space as well. Some valves need more clearance than others. If space is tight, you may need a compact design. Measure carefully to avoid future complications. Ultimately, thinking ahead can save you time and resources.
Material Selection for Knife Gate Valves
When selecting a knife gate valve, material choice is critical. The valve material must match the application conditions. For example, a corrosive environment requires a resilient material. Stainless steel and various alloys are common choices. These options can withstand harsh chemicals and ensure durability.
Consider the media type passing through the valve. Is it abrasive or viscous? This factor will influence material decision-making. If the media is abrasive, a material like hardened steel may be necessary. For more common applications, cast iron may suffice. The right material can prolong the valve's life, but sometimes you'll face limitations in availability.
Tips: Always inquire about the compatibility of materials with your specific media. Perform regular checks on valves in operation to catch early signs of wear. Be willing to rethink your choices based on performance feedback. A small oversight in material selection can lead to significant repair costs later. Assess your needs carefully, and consider consulting with a specialist if unsure.
How to Choose the Right Knife Gate Valve for Your Application? - Material Selection for Knife Gate Valves
| Material Type | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Range | Common Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Low | -20°C to 80°C | Water, wastewater | Cost-effective |
| Stainless Steel | High | -200°C to 600°C | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Durable, sanitary |
| PVC | Moderate | 0°C to 60°C | Chemical processing | Lightweight, easy to install |
| Ductile Iron | Moderate | -30°C to 100°C | Mining, slurry applications | Strength, impact resistance |
| Bronze | High | -50°C to 200°C | Marine applications | Corrosion-resistant, low friction |
Sizing and Pressure Rating Requirements for Knife Gate Valves
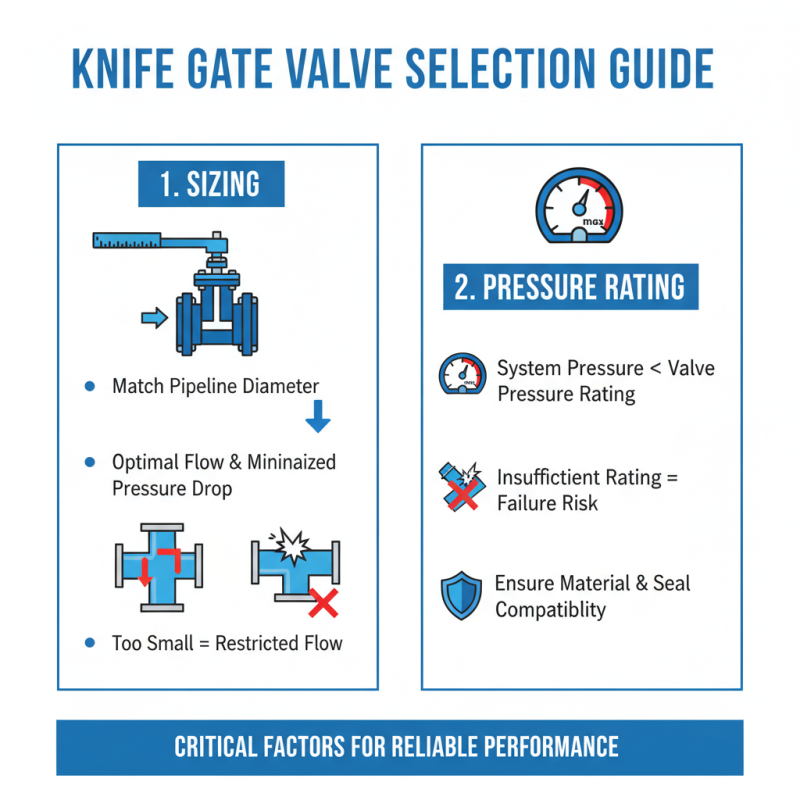
When selecting a knife gate valve, sizing and pressure rating are critical factors. The correct size ensures optimal flow and minimizes pressure drops. If the valve is too small, it can restrict flow. Alternatively, an oversized valve may lead to inefficiencies. Assess your pipeline's diameter and length to determine the appropriate size.
Pressure ratings indicate the valve's ability to withstand internal pressures. Common ratings are ANSI classes, like 150, 300, or 600. Each rating corresponds to specific pressure limits. Knowing your application’s pressure requirements helps in making the right choice. Overlooking this can lead to valve failure or leaks.
Tips: Always consult technical documents before purchasing. Check if the valve meets your application demands. Regularly review your system’s pressure levels. This can prevent unexpected issues. Remember that some valve materials are better suited for certain conditions. Adjust your choices based on the actual environment where the valve will be used.
Maintenance and Reliability of Knife Gate Valves
Knife gate valves are essential in various industries. Their maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring reliability. A well-maintained valve minimizes downtime and costly repairs. Failing to inspect the valve regularly can lead to significant issues. Buildups and debris can affect performance and longevity.
Regular cleaning is vital. Accumulated materials can block the flow and damage seals. Operators often neglect this step. It’s easy to overlook the simple tasks. Inspecting for leaks or rust can prevent larger problems. Timely replacement of worn parts is essential for smooth operation. Neglecting this can mean facing unexpected failures.
Training staff on proper use enhances reliability. Many accidents occur due to misuse. Operators should know how to operate and maintain these valves. It’s important to create an environment where maintenance is a priority. A proactive approach saves time and money in the long run. Ignoring small problems often leads to bigger headaches later.
Related Posts
-

Maximizing Operational Efficiency: The Role of Knife Gate Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Knife Gate Valve for Your Industrial Application
-

Top 5 Pneumatic Valves to Watch in 2025: Features and Applications
-
Top 10 Globe Valves Types and Their Applications in Industrial Systems You Should Know
-

How to Choose the Right Spring Check Valve for Your Application?
-
Top Motorized Valves for 2025 Which One is Right for Your Needs
