Blog
Understanding Motorized Valves: Essential Components for Efficient Fluid Control Systems
In today's industrial landscape, the importance of precise fluid control cannot be overstated, as it directly influences operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
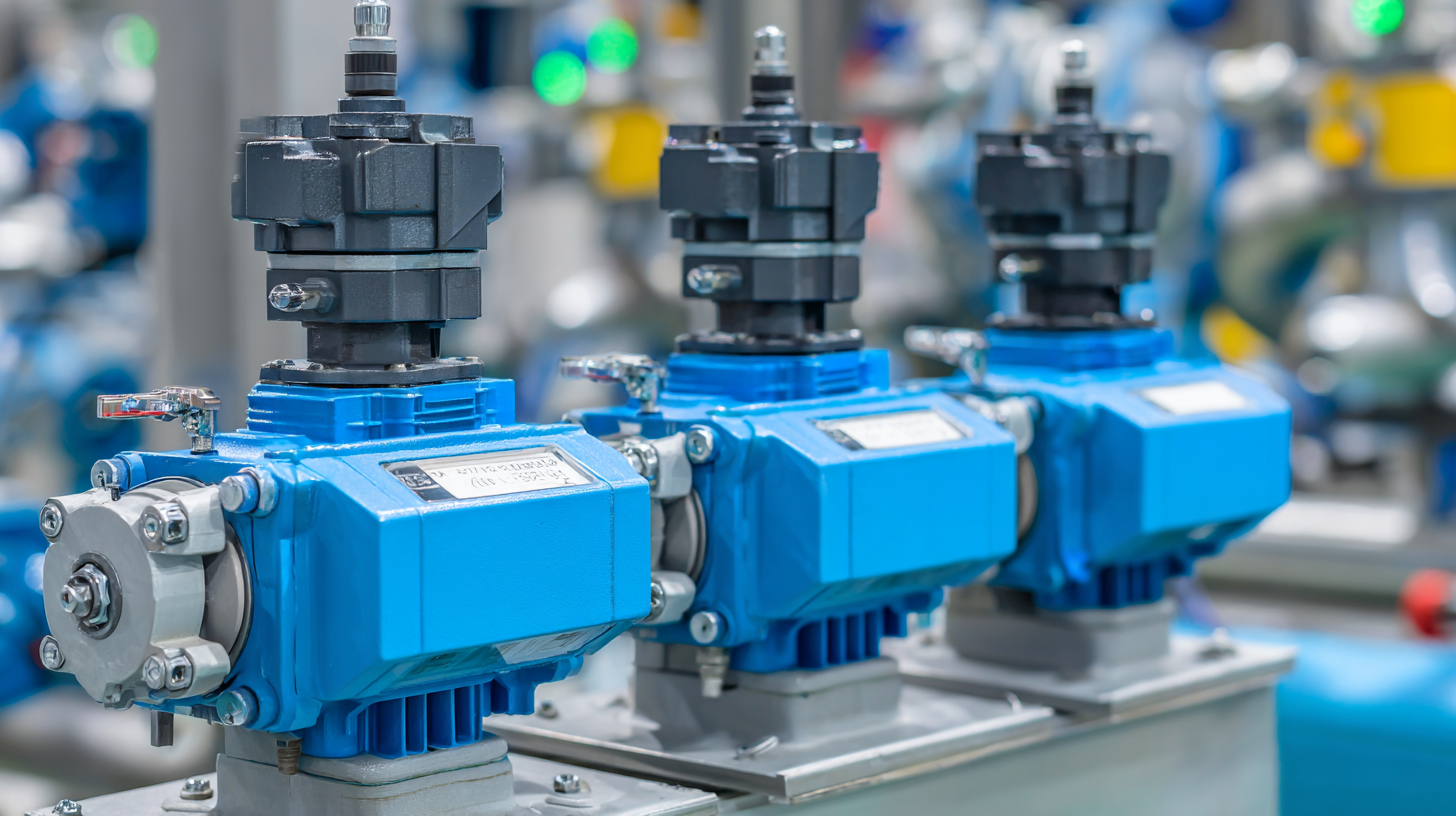 Motorized valves, pivotal in regulating the flow and pressure of liquids and gases in various systems, have seen a significant rise in demand. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global motorized valve market is projected to grow from USD 2.5 billion in 2020 to USD 3.5 billion by 2025, reflecting an annual growth rate of 7.2%.
This growth is attributed to the increasing need for automation in industrial processes and the growing emphasis on efficient energy management.
Understanding the essential components and operational mechanisms of motorized valves is crucial for engineers and system designers aiming to optimize performance and reliability in fluid control applications.
This article will delve into the key aspects of motorized valves, providing insights and practical guidance for their effective implementation in modern fluid management systems.
Motorized valves, pivotal in regulating the flow and pressure of liquids and gases in various systems, have seen a significant rise in demand. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global motorized valve market is projected to grow from USD 2.5 billion in 2020 to USD 3.5 billion by 2025, reflecting an annual growth rate of 7.2%.
This growth is attributed to the increasing need for automation in industrial processes and the growing emphasis on efficient energy management.
Understanding the essential components and operational mechanisms of motorized valves is crucial for engineers and system designers aiming to optimize performance and reliability in fluid control applications.
This article will delve into the key aspects of motorized valves, providing insights and practical guidance for their effective implementation in modern fluid management systems.
Choosing the Right Type of Motorized Valve for Your System Needs
When selecting the right type of motorized valve for your fluid control system, it's crucial to consider both the operational requirements and the specific application needs. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global motorized valve market is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2025, indicating strong growth driven by increasing automation in industries such as water treatment, HVAC, and oil and gas. Factors like pressure ratings, temperature ranges, and fluid types should be meticulously evaluated to ensure optimal valve performance.
Different types of motorized valves serve various functions; for instance, electric and pneumatic valves each have unique advantages. Electric motorized valves are ideal for precise flow control, offering easy integration with electronic control systems, which is essential for applications requiring a high degree of automation. Meanwhile, pneumatic valves excel in environments where quick actuation is necessary, making them a preferred choice for safety applications in chemical processing. By aligning the specific requirements of your system with the appropriate motorized valve technology, you can enhance efficiency and reliability in fluid control operations.
Key Components of Motorized Valves: Understanding Their Functions
Motorized valves are integral components in fluid control systems, designed to regulate the flow of liquids and gases efficiently. These valves operate through an electric actuator that opens or closes the valve mechanism, allowing for precise control over the flow rates and pressure levels in a system. A key component of motorized valves is the actuator itself, which can be either linear or rotary depending on the type of valve. The actuator's design directly impacts its performance and response time, making it critical to select the appropriate actuator for specific applications.
Another essential element of motorized valves is the valve body, which houses the internal mechanisms and provides the physical structure necessary for operation. The materials used in the valve body are crucial, as they must withstand the operating conditions, including temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid being controlled. Additionally, feedback sensors and control circuitry play a vital role in enhancing the functionality of motorized valves, allowing for automated adjustments and monitoring of flow conditions. Together, these components ensure that motorized valves operate efficiently and reliably within fluid control systems.
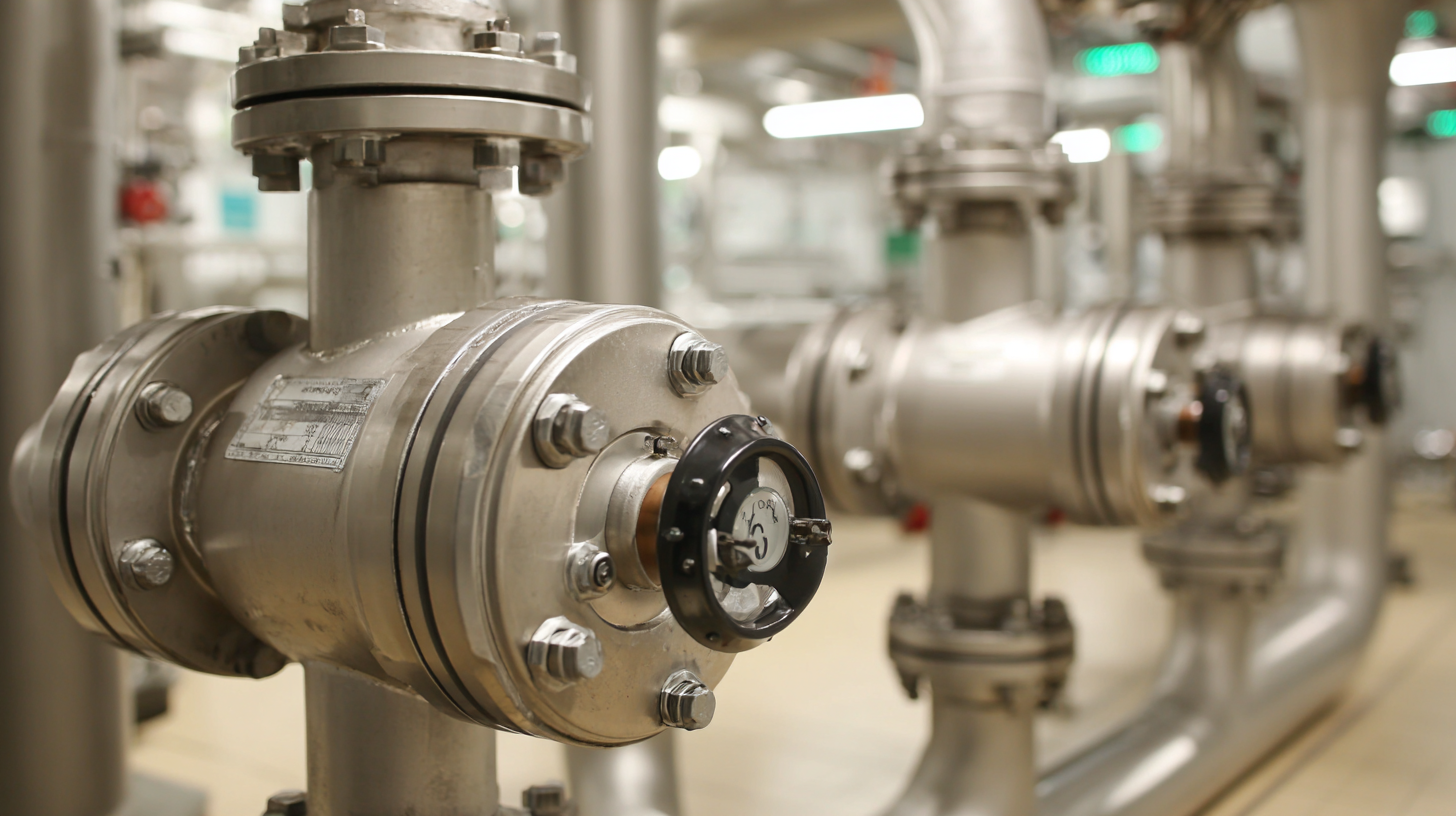

Installation Tips for Motorized Valves in Fluid Control Applications
When installing motorized valves in fluid control systems, careful attention to detail is crucial for seamless operation. Begin by selecting the appropriate valve type that matches the fluid properties and system requirements. It is essential to consider factors such as pressure, temperature, and compatibility with the fluid to ensure optimal performance. Before the installation starts, gather all necessary tools and materials, ensuring that you have the appropriate fittings and seals to avoid leaks.
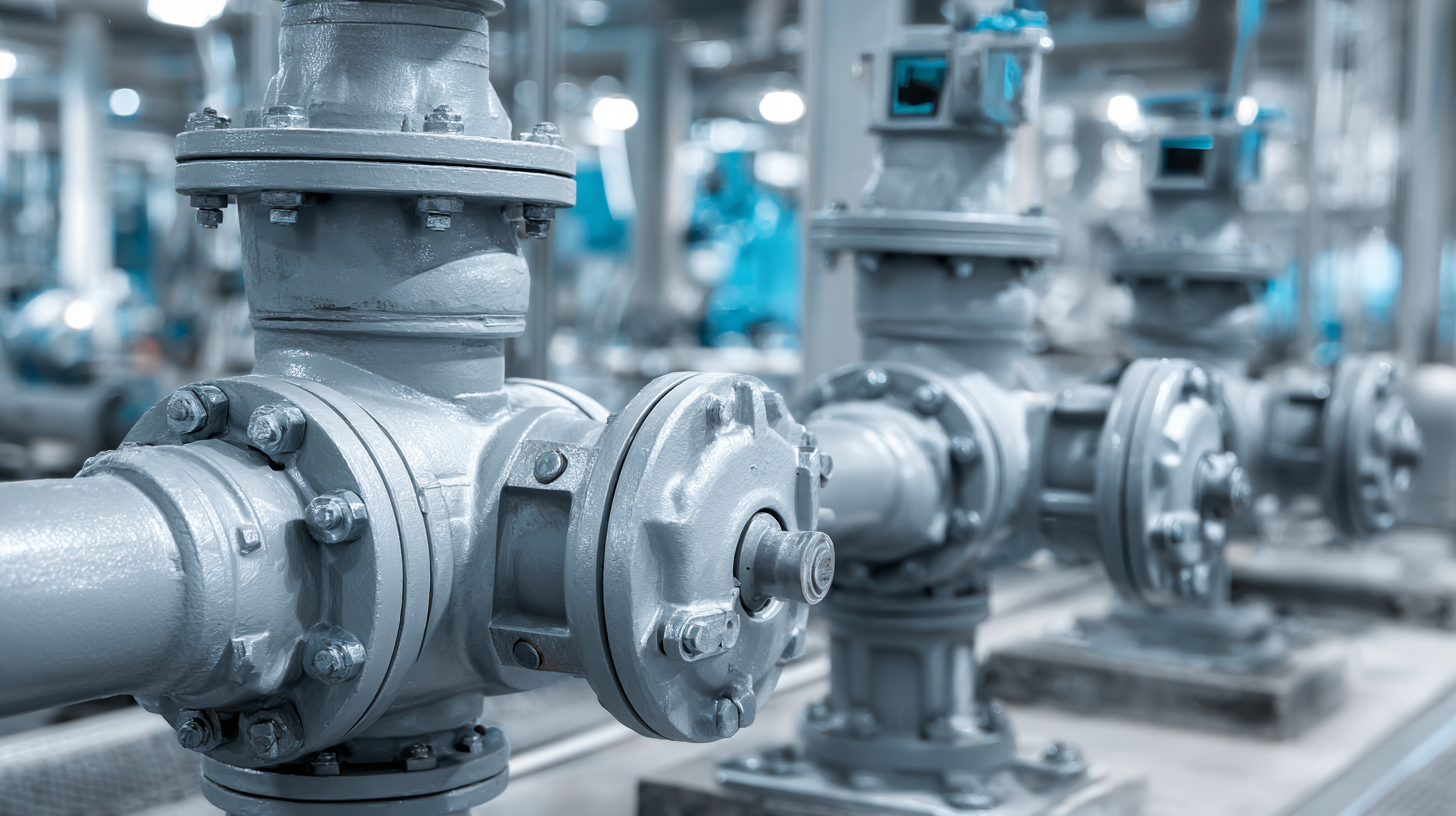

Proper positioning of motorized valves cannot be overstated. Ensure the valve is installed in a location that allows easy access for maintenance and inspection. When mounting the valve, follow the manufacturer's guidelines regarding orientation; for instance, some valves perform better when installed in horizontal positions. Additionally, focus on aligning the valve with the piping system to prevent unnecessary stress on the valve components. Once installed, conduct thorough testing to verify correct operation and make adjustments as needed, confirming that the valve effectively regulates fluid flow within the system.
Maintaining Motorized Valves: Best Practices for Longevity and Performance
Maintaining motorized valves is crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance in fluid control systems. Regular inspection and cleaning are fundamental practices that can prevent debris accumulation and potential blockages. It is essential to check electrical connections, ensuring they are secure and free from corrosion. Periodic testing of response times and operational efficiency can help identify any emerging issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Furthermore, lubrication of moving parts is vital to minimize wear and tear. Applying the correct lubricants helps maintain smooth operation and prevents mechanical failure. Additionally, monitoring the operating environment—such as temperature and pressure—can also affect valve performance. Maintaining the manufacturer's recommended specifications for these conditions ensures that the motorized valves function properly throughout their lifespan. Proper training for personnel involved in maintenance tasks can lead to a more effective maintenance routine, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and longevity of the fluid control systems.
Understanding Motorized Valves: Essential Components for Efficient Fluid Control Systems
| Component | Function | Material | Maintenance Frequency | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actuator | Controls valve movement | Aluminum, plastic | Quarterly | Overheating, noise |
| Valve Body | Regulates flow | Stainless steel, brass | Annually | Corrosion, wear |
| Gaskets | Provides sealing | Rubber, PTFE | Semi-Annually | Leakage, deterioration |
| Positioner | Controls valve position | Plastic, metal | Once a Year | Calibration failure |
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Motorized Valve Operation
When dealing with motorized valves, troubleshooting common issues is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of fluid control systems. One frequent problem is the valve not opening or closing correctly, which may stem from power supply issues or mechanical obstructions. A thorough inspection of the power connections and ensuring the actuator receives the correct voltage can help identify electrical faults. Additionally, physical blockages due to debris or wear can hinder valve movement, necessitating routine maintenance and cleaning.
Another common issue is the valve responding slowly or erratically. This can often be attributed to improper calibration or control signal interference. Ensuring that the control signal is stable and accurately calibrated can mitigate responsiveness issues. Furthermore, checking the pneumatic or hydraulic supply lines for leaks or pressure drops is essential, as these can affect performance. Regular diagnostics and preventive measures not only enhance the reliability of motorized valves but also prolong their service life, ensuring optimal operation within fluid control systems.
Understanding Motorized Valves: Operational Issues and Troubleshooting
This bar chart illustrates the frequency of common operational issues in motorized valves based on industry data.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Role of Spring Check Valves in Modern Fluid Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
-

Understanding the Importance of Spring Check Valve in Modern Plumbing Systems
-

Exploring Pneumatic Rotary Actuator Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Why Pneumatic Rotary Actuators Are Essential for Modern Automation
-

Exploring the Future of Basket Strainers at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Valve for Your Industrial Application
