Blog
Top Tips for Choosing Pneumatic Valve Actuators?
Choosing the right pneumatic valve actuator is crucial for system efficiency. These actuators control the opening and closing of valves, impacting fluid flow. Selecting the wrong actuator can lead to performance issues.
Consider the operating environment. Conditions like temperature and pressure can affect actuator performance. Compatibility with the chosen valve types is also important. Different valves require specific actuator types to function properly.
Evaluate reliability and maintenance needs. Some pneumatic valve actuators are more durable than others. Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected downtime. Make sure you invest in an actuator that suits your long-term goals.

Understanding Pneumatic Valve Actuators: Types and Their Applications
Pneumatic valve actuators play a crucial role in various industrial applications. These devices convert compressed air into mechanical motion, enabling the control of valves. There are several types of pneumatic valve actuators, each suited for different tasks. Linear and rotary actuators are the most common. Many industries rely on these actuators to manage processes effectively.
The application of pneumatic actuators is widespread. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global pneumatic valve actuator market is expected to reach $15 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6%. This growth highlights the importance of selecting the right actuator type. Factors such as speed, force, and valve size must be considered. In some cases, users may overlook the actuator’s compatibility with existing infrastructure.
In practice, issues may arise if selections are not carefully made. For instance, using an actuator with insufficient torque might lead to valve failure. This can cause process disruptions. It’s essential to assess performance data before committing. An informed choice can significantly enhance operational efficiency in industries ranging from manufacturing to oil and gas. Understanding specific application needs is vital for optimal performance.
Evaluating Key Specifications: Torque, Speed, and Pressure Ratings
When choosing pneumatic valve actuators, evaluating key specifications is crucial. Torque is one of the primary factors. It determines how much force the actuator can exert. Typically, actuators are rated between 30 Nm to 300 Nm. Some applications may demand higher torque. Thus, understanding your system's requirements is essential.
Speed is another vital specification. Pneumatic actuators can operate at speeds of up to 2000 cycles per hour. However, higher speeds often lead to increased wear on components. Maintaining a balance between speed and durability is crucial. It's worthwhile to consider the impact of varying speeds on overall system performance.
Pressure ratings should also be scrutinized closely. Most systems operate effectively within a range of 0.2 to 1.0 MPa. If pressure ratings are not met, performance can decline sharply. Often, users overlook these critical parameters, leading to premature actuator failure. Choosing the right specifications can be complex. It requires careful analysis and sometimes, trial and error.
Material Selection for Durability: Corrosion Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
When selecting pneumatic valve actuators, material choice is crucial. Corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance are vital factors. Corrosive environments can quickly degrade materials. This can lead to actuator failure. Choosing a resistant material can ensure longevity and reliability.
Stainless steel is a popular choice. It offers excellent corrosion resistance. However, it might not be enough for extreme conditions. In some cases, coatings can provide additional protection. These coatings can resist harsher chemicals. Yet, they can wear off over time, requiring maintenance.
Temperature tolerance is another essential aspect. Some materials can handle extreme heat. Others don't fare well in cold environments. Using the wrong material can result in malfunction. It’s wise to test materials in real-world conditions. Think about long-term effects. A well-chosen material can lead to fewer problems down the road.
Top Tips for Choosing Pneumatic Valve Actuators
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Tolerance (°C) | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent | -40 to 200 | Chemical Processing |
| Aluminium | Good | -20 to 150 | Food & Beverage |
| Brass | Moderate | -10 to 120 | Water Systems |
| Plastic (PVC) | Fair | 0 to 60 | Low Pressure Applications |
| Carbon Steel | Low | -20 to 100 | Industrial Uses |
Importance of Control Mechanisms: Digital vs. Analog Actuator Controls
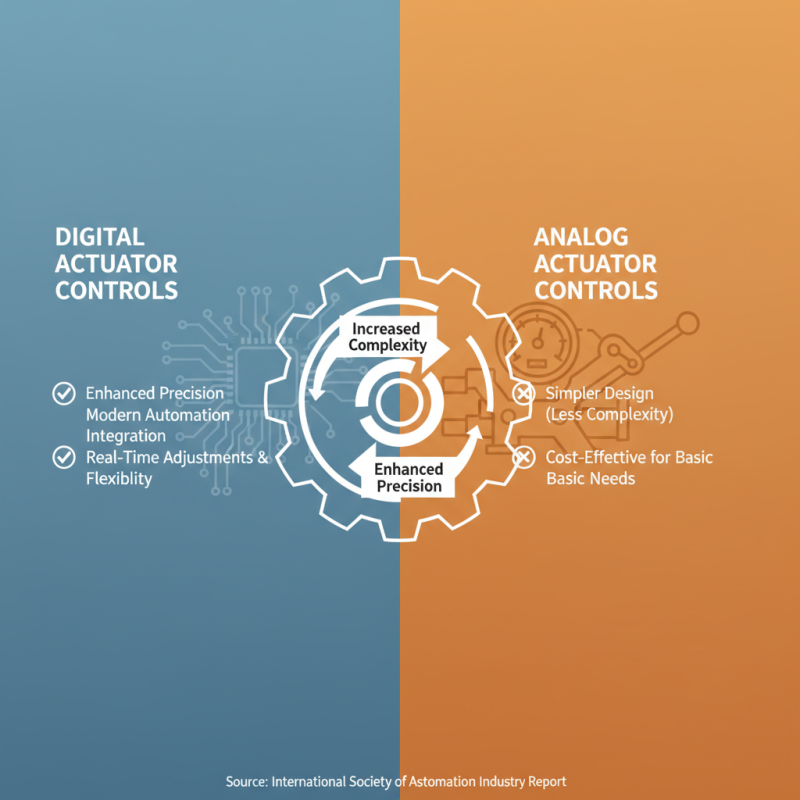
When selecting pneumatic valve actuators, the control mechanisms play a crucial role. Digital and analog actuator controls each have unique advantages and limitations. A recent industry report by the International Society of Automation indicates that digital controls can provide enhanced precision. They offer better integration with modern automation systems. This facilitates real-time adjustments and greater flexibility. However, it can also lead to increased complexity, which isn't always necessary.
On the other hand, analog actuator controls are simpler and often more reliable. They do not rely on software, making them easier to troubleshoot. According to a study by the hydraulic and pneumatic industry, nearly 40% of facilities that used analog controls reported lower maintenance costs over five years compared to those using digital systems. But the downside is that analog systems may lack the advanced features required for specific applications.
Choosing between digital and analog controls depends on your operational needs. Each system can perform well under the right conditions. Yet, the decision could impact efficiency, cost, and downtime. Revisiting your control strategy can be beneficial. Relying too heavily on one type might lead to performance issues in the long run. If your needs change, being locked into a single control type could hinder your ability to adapt.
Maintenance Best Practices: Ensuring Longevity and Optimal Performance
Maintaining pneumatic valve actuators is crucial for their longevity. Regular inspection is key. Look for signs of wear or leaks. Small issues can grow into major problems. A simple visual check can save time and money. Don’t ignore the importance of keeping them clean. Dust and debris can hinder performance.
Lubrication is essential but can be tricky. Too much grease may attract dirt, while too little leads to wear. Find the right balance. Also, monitor the actuator's response time. Delays may indicate wear. If you notice unusual sounds, it’s time to investigate.
Document all maintenance activities. This practice helps track performance over time. Create a schedule for regular checks. A reactive approach often leads to unexpected breakdowns. Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is more effective. Consider training staff on proper handling. Misuse can lead to premature failures. Remember, small details matter in upkeep.
Related Posts
-

Why Pneumatic Rotary Actuators Are Essential for Modern Automation
-

Exploring Pneumatic Rotary Actuator Innovations at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Actuator for Your Application in 2025
-

Why Understanding Pneumatic Flow Control Valves is Essential for Efficient Industrial Processes
-

Best Pneumatic Flow Control Valve Options for Efficient Fluid Management
-
2026 How to Choose the Best Pneumatic Rotary Actuator for Your Needs?
